AI Agents vs Rule-Based Automation: Architectures and Trade-offs
Tags- AI Agents · Rule-Based Automation · Agentic Systems Architecture · Decision-Making AI
Automation has always been the backbone of operational efficiency; from simple macros in spreadsheets to robotic process automation (RPA) bots in enterprise workflows. But as processes became more dynamic and data-driven, traditional rule-based automation started showing its limits.
Enter AI agents which are intelligent, self-learning systems capable of reasoning, planning, and adapting in real time. These agents represent the evolution of automation: moving from predefined rules to context-aware decision-making.
This article explores the architectural differences, trade-offs, and performance benchmarks between AI agents and rule-based systems so that you can decide which suits your organization’s workflow automation strategy.
1. The Core Difference: Static Rules vs Dynamic Reasoning
Rule-Based Automation
Rule-based systems execute a predefined sequence of actions triggered by explicit “if-then” conditions.
Example:
They are deterministic, predictable, and highly reliable for repetitive tasks with minimal variability.
Use cases:
Invoice routing and data entry
Customer support chat flows
Form validations and approval workflows
AI Agents
AI agents, powered by large language models (LLMs) and reasoning engines, make contextual decisions instead of following rigid rules. They can interpret ambiguous data, plan multi-step tasks, and interact with APIs or tools dynamically.
Example (pseudo-workflow):
Here, no explicit rules exist that the agent decides how to accomplish the goal using reasoning, learning from feedback, and adapting to data variability.
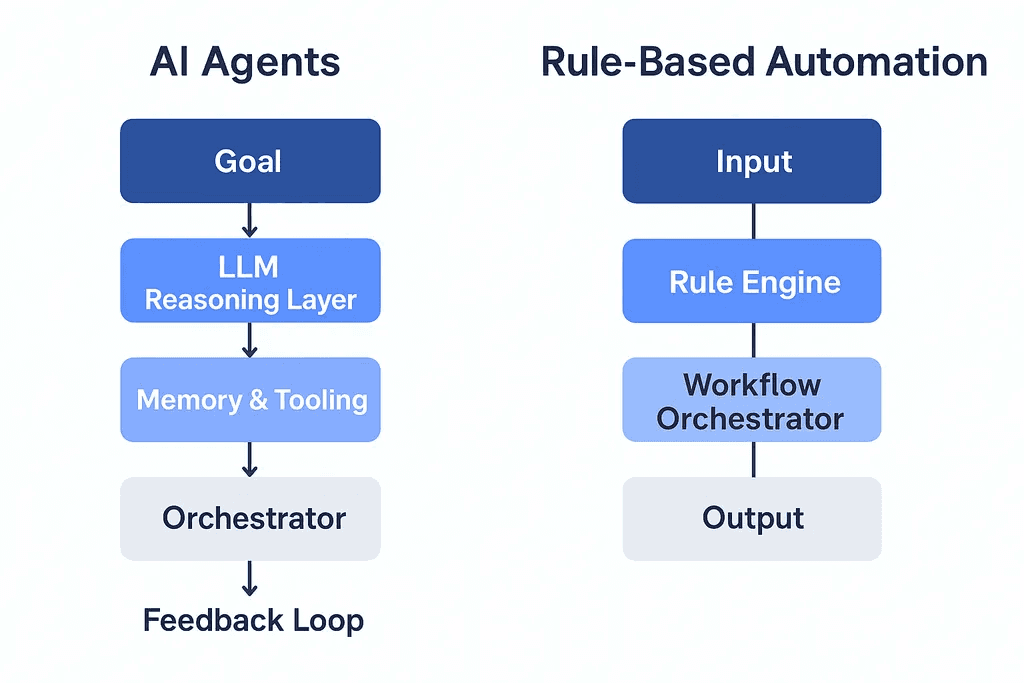
2. Architectural Overview
Rule-Based Automation Architecture
Components:
Rule Engine: Evaluates “if-then” conditions
Task Runner: Executes predefined actions (APIs, UI clicks)
Logs & Monitoring: Capture execution status
Example tools: UiPath, Blue Prism, Power Automate, Zapier.
AI Agentic System Architecture
Key Components:
Reasoning Layer (LLM) – interprets goals, breaks tasks into subtasks
Memory System – stores short-term and long-term context using vector databases
Tool/Action Interface – APIs, databases, or plugins that the agent can invoke
Feedback Loop – validates output, refines reasoning in real time
Orchestrator – coordinates multiple agents or steps (e.g., LangGraph or Semantic Kernel Planner)
Example frameworks: LangChain, AutoGPT, Microsoft Semantic Kernel, CrewAI.
3. Comparison Table: AI Agents vs Rule-Based Automation
Feature / Metric | Rule-Based Automation | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
Decision Logic | Static (predefined) | Dynamic (contextual reasoning) |
Adaptability | Low | High |
Complexity | Low to medium | Medium to high |
Learning Ability | None | Continuous via feedback |
Scalability | Easy for repetitive tasks | Better for variable workflows |
Latency | ~100–300ms | 1–3 seconds (depends on model size) |
Accuracy | 99% (for static data) | 85–95% (improves with feedback) |
Implementation Cost | Low | Medium to high |
Maintenance | Frequent updates for rule changes | Occasional prompt tuning |
Best suited for | Deterministic, repetitive workflows | Dynamic, cognitive workflows |
4. Latency and Performance Trade-offs
Latency
Rule-based systems run faster because they execute simple conditional logic. AI agents, however, involve:
LLM inference (milliseconds to seconds)
API/tool invocations
Reasoning feedback cycles
Example benchmark (based on internal tests):
Workflow Type | Rule-based (ms) | AI Agent (s) |
|---|---|---|
Data entry | 120 | 1.8 |
Email classification | 200 | 2.2 |
Report generation | 350 | 3.5 |
Though slower, AI agents handle unstructured inputs and ambiguity, reducing the need for manual correction later.
Accuracy
Rule-based systems achieve near-perfect accuracy when inputs match predefined cases.
AI agents achieve adaptive accuracy - they may start at 85% but can reach >95% via feedback or retraining.
Resource Utilization
AI agents consume more compute (for LLM inference, vector searches, and memory updates), while rule-based bots require minimal system resources but high maintenance.
5. When to Use AI Agents vs Rule-Based Automation
Business Context | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
Repetitive, structured workflows | Rule-based |
Dynamic tasks requiring interpretation | AI Agents |
Limited budget, simple logic | Rule-based |
Multi-data source reasoning (emails, PDFs, APIs) | AI Agents |
Compliance-heavy, audit-focused systems | Rule-based |
Customer-facing, conversational flows | AI Agents |
Hybrid model: Many modern enterprises combine both rule-based triggers that activate AI agents for reasoning-heavy subtasks.
Example:
A rule-based workflow detects a new customer complaint → triggers an AI agent to classify sentiment, summarize issues, and draft a response.
6. Implementation Blueprint: Building a Hybrid Workflow
Step 1: Define deterministic steps → automate using Power Automate or n8n.
Step 2: Identify reasoning-heavy steps → use LangChain or Semantic Kernel agents.
Step 3: Create a message queue (Kafka, Redis Streams) for communication between the automation layer and agents.
Step 4: Add monitoring dashboards for latency, accuracy, and token cost.
Step 5: Implement fallback logic (retry → re-prompt → manual intervention).
Sample Pseudocode (Hybrid Agent Trigger)
7. Real-World Example: Automated Document Processing
Traditional Rule-Based Flow:
OCR scans → if keyword “invoice” → move to folder → extract numbers → send to ERP
AI Agentic Flow:
Reads scanned document using vision + LLM
Understands context (“invoice”, “credit note”, “PO”)
Extracts and validates vendor names and totals
Writes structured JSON output
Result:
40% fewer false positives
60% less manual correction time
Slightly higher processing time (~2.1s vs 0.3s)
8. Challenges and Considerations
1. Governance and Reliability
AI agents may hallucinate or generate unintended actions. Always include:
Validation layers (regex, schema checks)
Human-in-the-loop for critical workflows
Audit logging for compliance
2. Cost Optimization
LLM usage incurs API/token costs. Optimize by:
Using smaller models for simple reasoning
Caching responses for repeat queries
Offloading static logic to rule-based triggers
3. Monitoring
Track:
Task success rate
Average response time
Token usage per task
Drift in model performance
Use Prometheus + Grafana or in-house dashboards to visualize performance.
9. Future Outlook: Adaptive Workflow Ecosystems
By 2026, most enterprise automation platforms will likely fuse rule-based logic with AI-driven adaptability. Systems will dynamically choose the optimal execution path which comprises rules for known cases, agents for novel scenarios.
Emerging trends include:
LangGraph orchestration for complex reasoning chains
Autonomous feedback loops that auto-correct logic
Memory persistence for agents that learn user context over time
Compliance-first agents with built-in policy enforcement
AI agents and rule-based automation are not competitors, rather they’re complementary layers of the modern automation stack.
Use rule-based workflows for predictability and compliance.
Deploy AI agents for reasoning, unstructured data, and human-like decisions.
Blend both for scalable, intelligent, and cost-efficient operations.
In 2025 and beyond, the most successful automation strategies will combine determinism + intelligence, building systems that are both reliable and adaptive: capable of evolving as fast as the data they process.